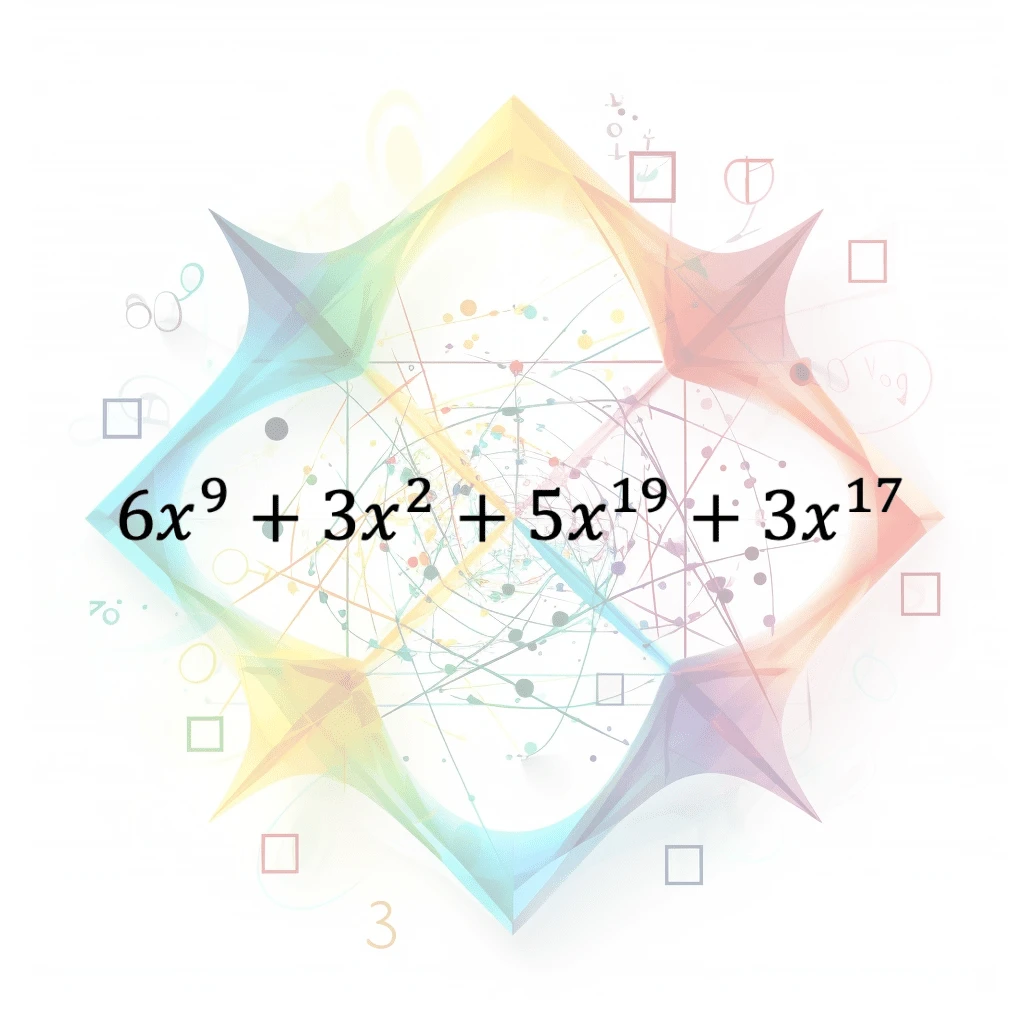
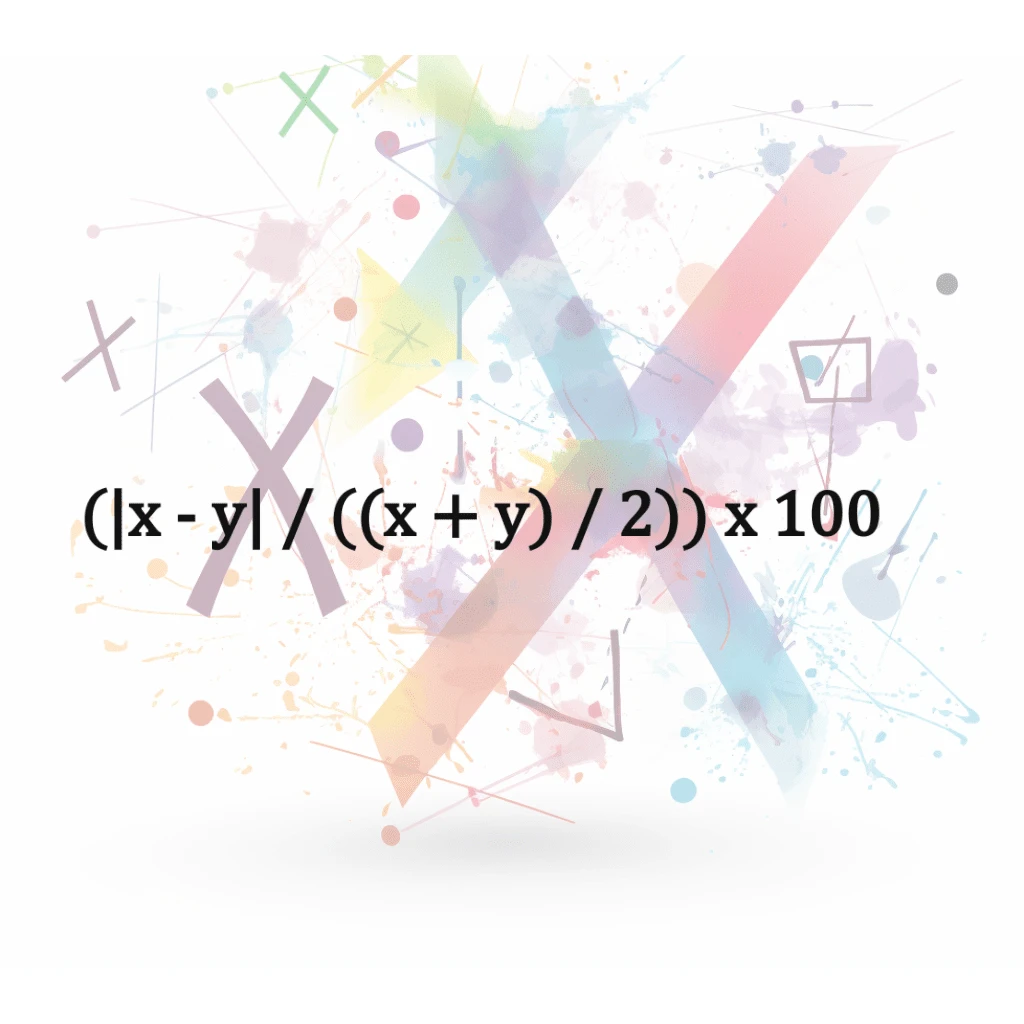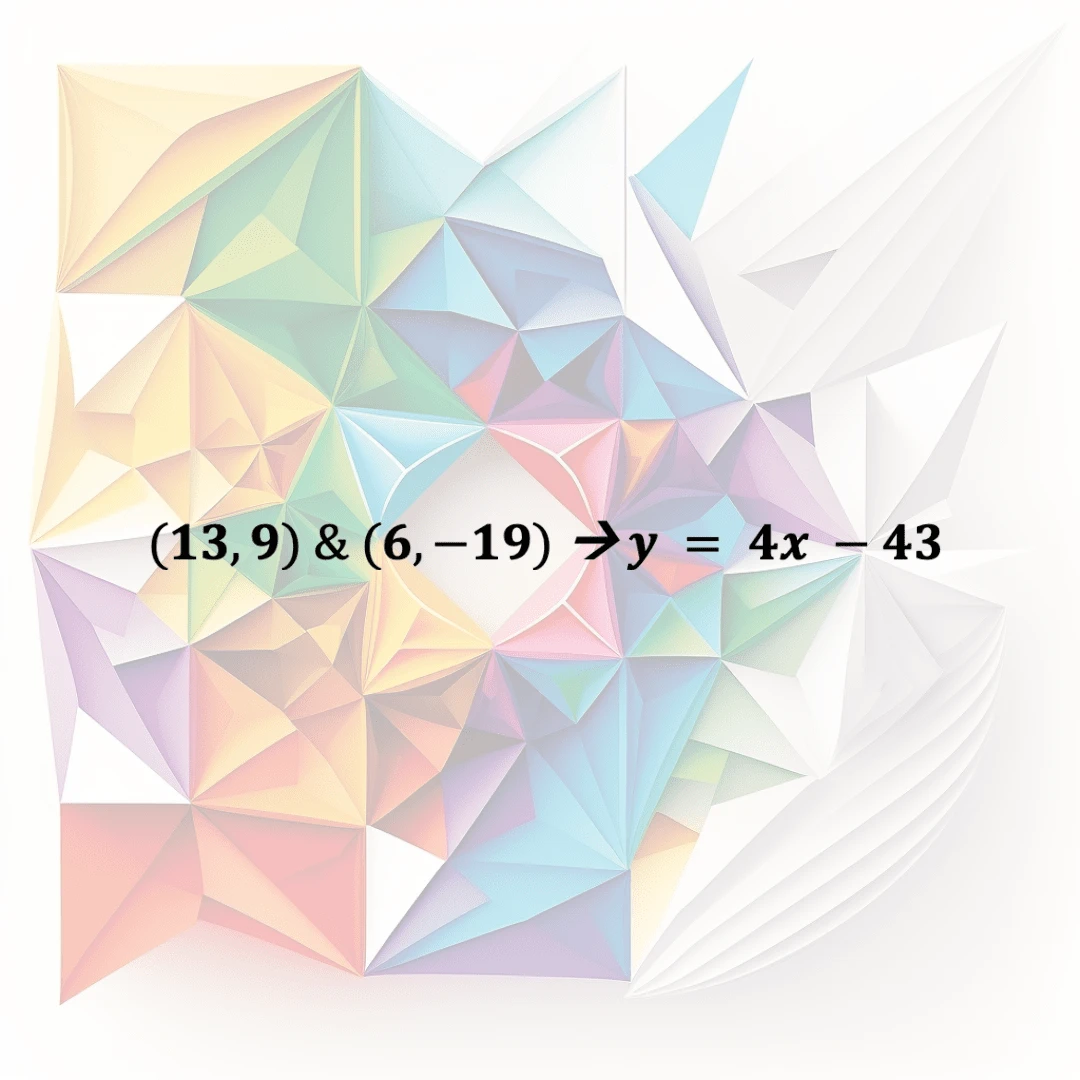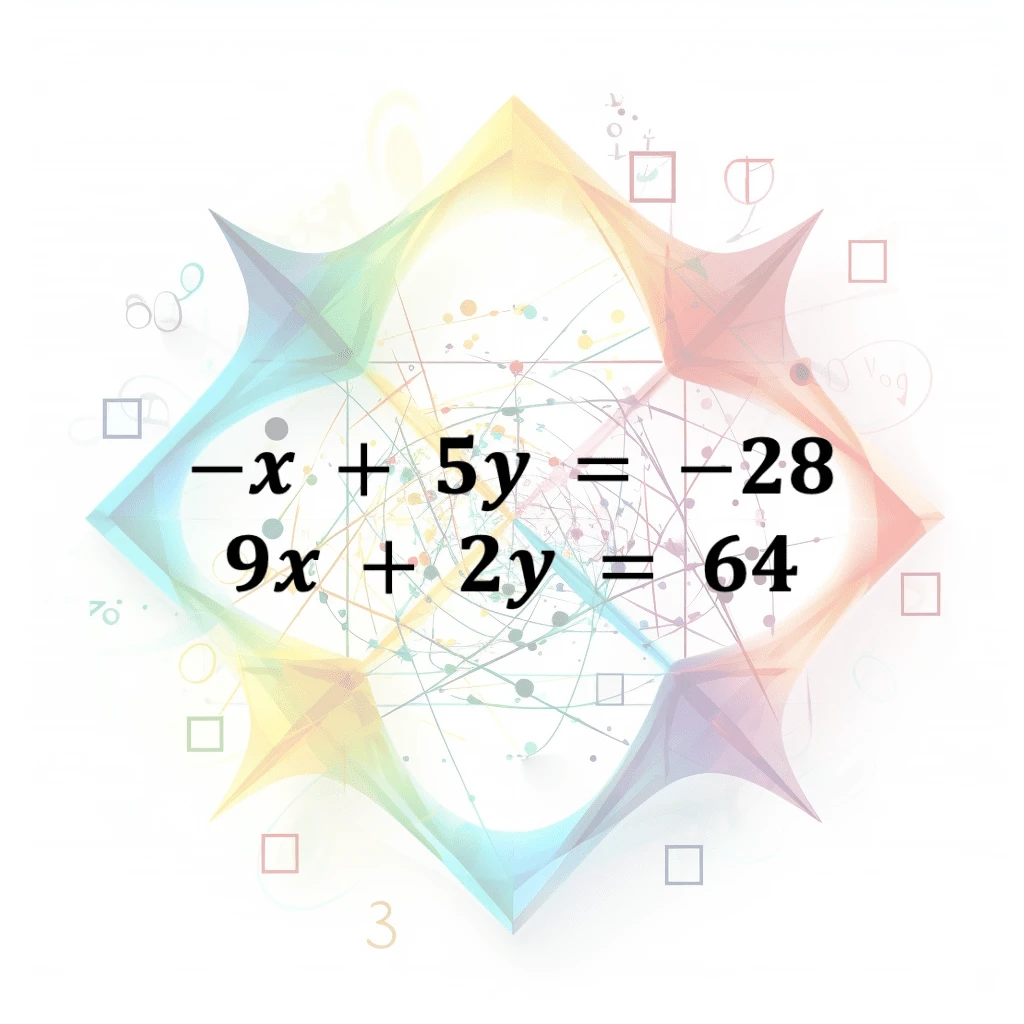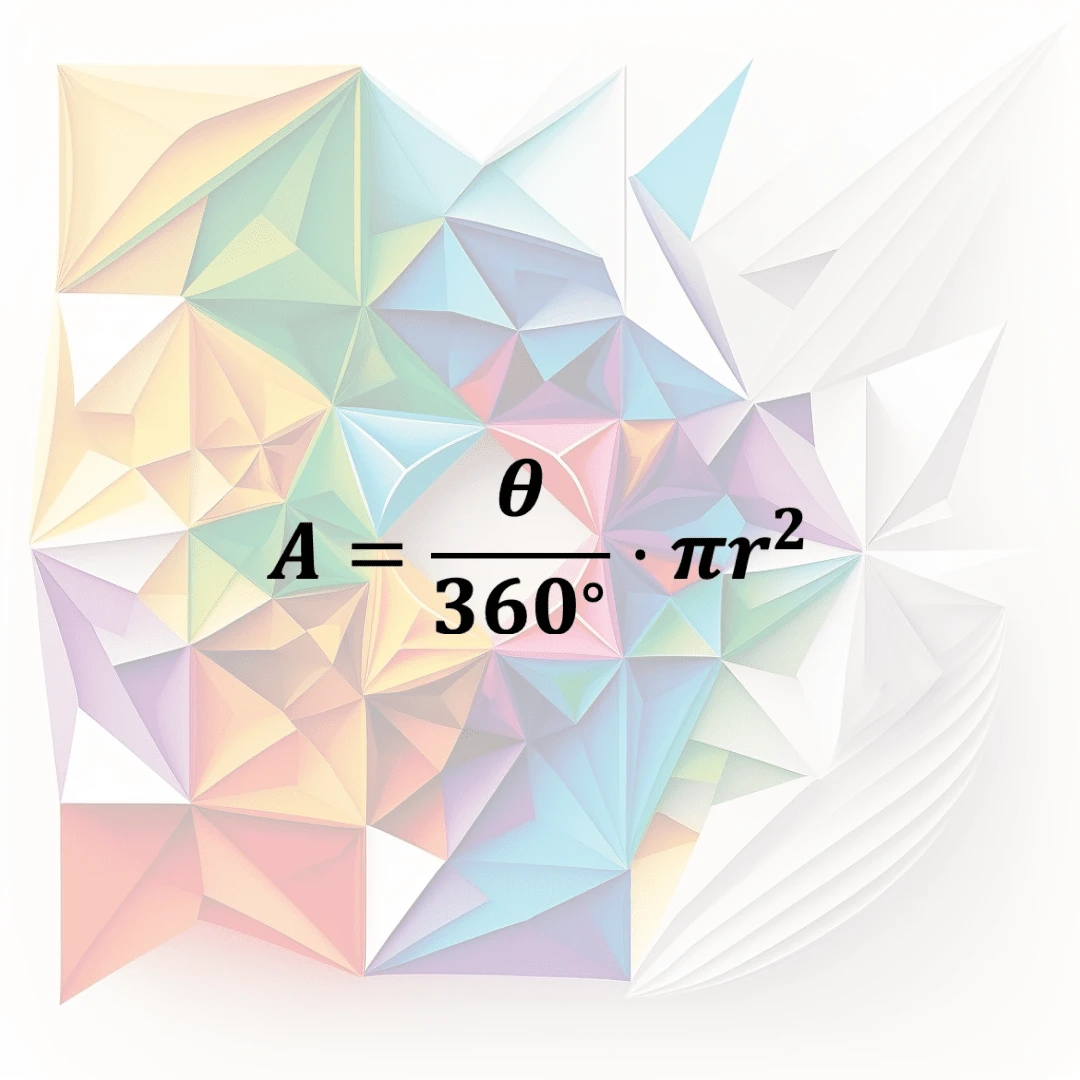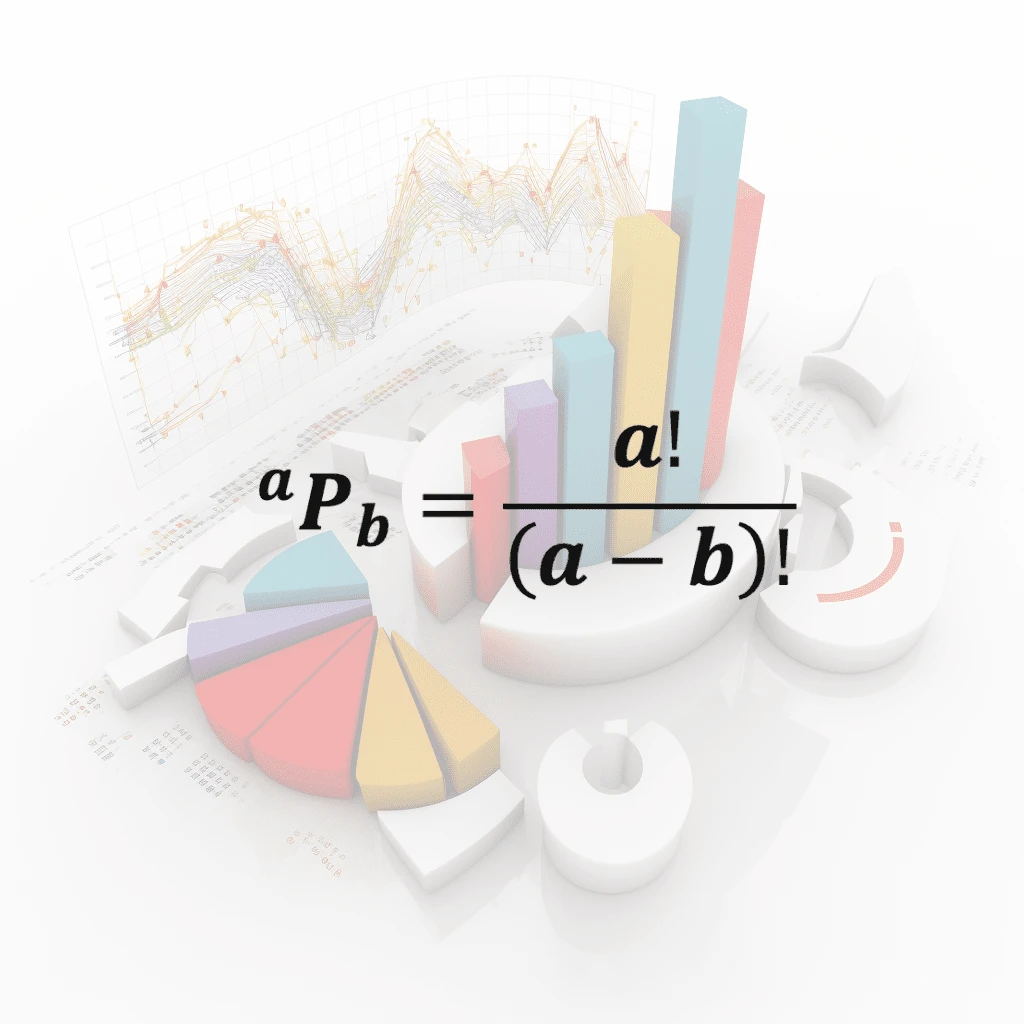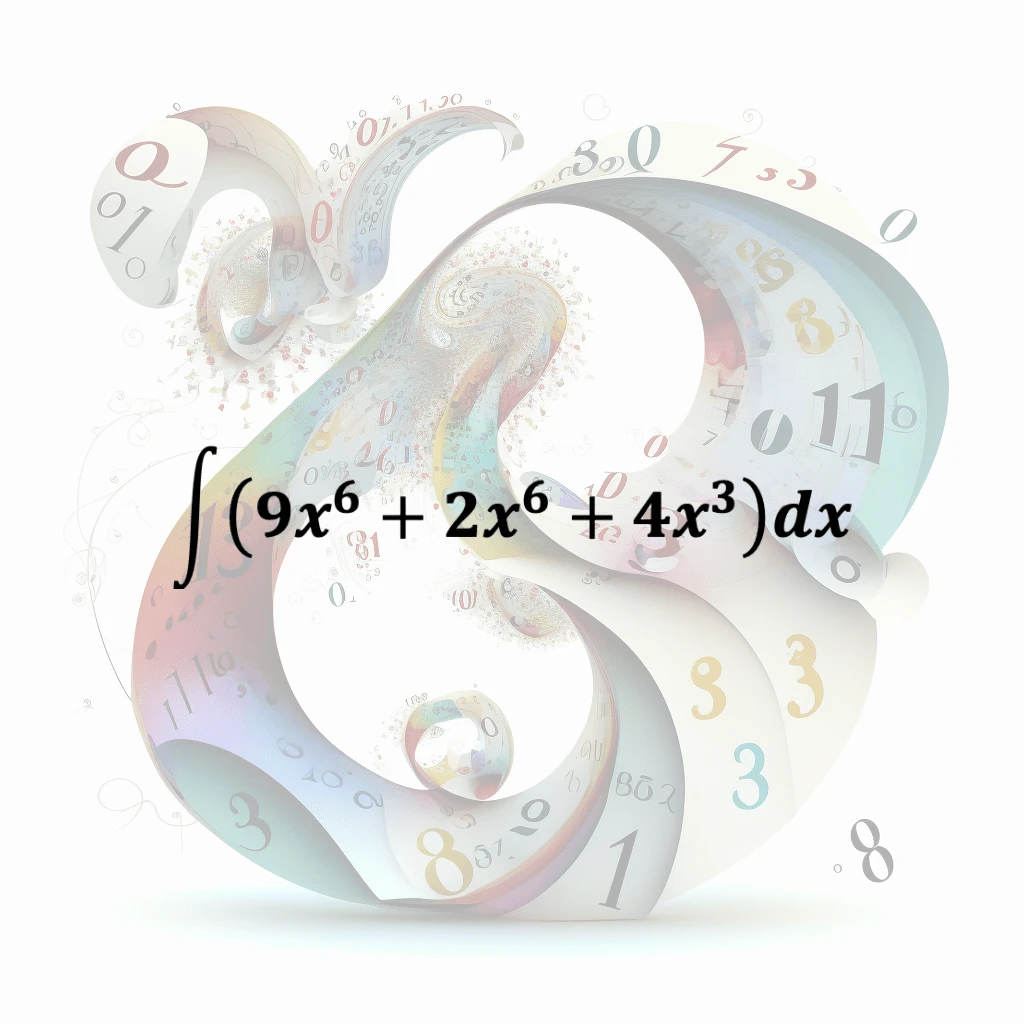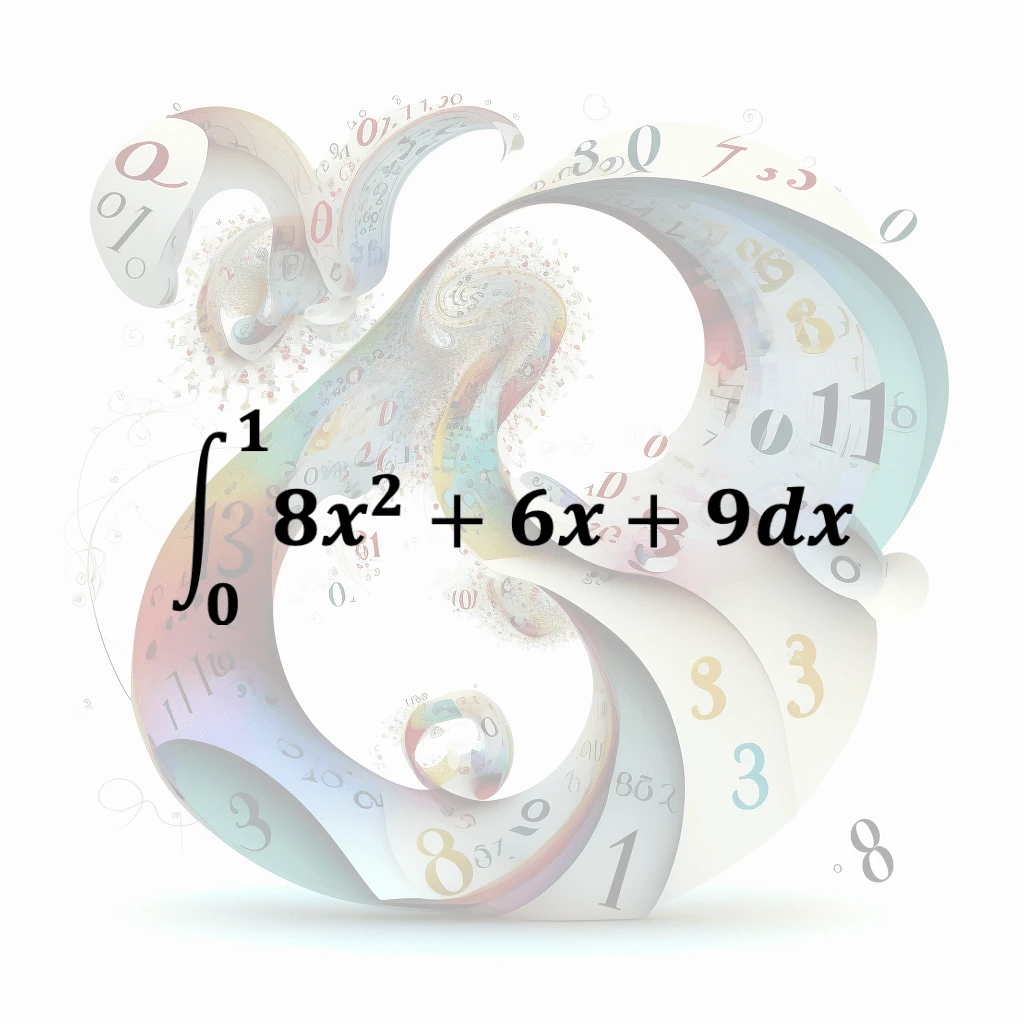Combine Like Terms
in algebra, combining like terms is the process of simplifying an expression by combining terms that have the same variables and exponents. For example, in the expression 3x + 2y + 5x - 4y, the like …
Percentage Difference
The percentage difference is the difference between two numbers expressed as a percentage of the original number. For example, if the original number is 100 and the difference between that number and…
Percentage Error
The percentage error is the difference between an estimated value and the actual value expressed as a percentage of the actual value. For example, if you estimate the weight of an object to be 10 pou…
Equation Of Line From Two Poi…
The equation of a line from two points is the formula for finding the equation of a straight line when given two points on the line.
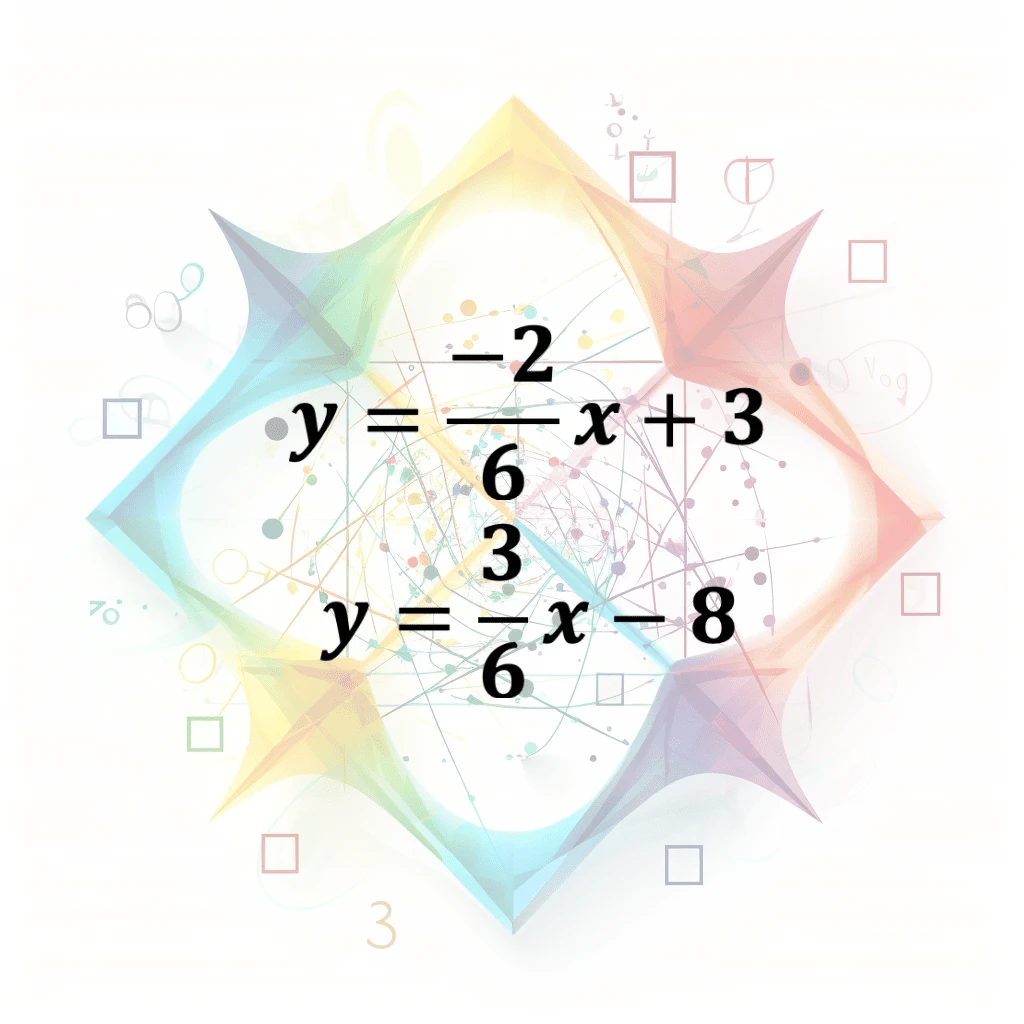
System Of Equations
A collection of two or more equations with multiple unknown variables that are solved together to find the values of the unknowns that satisfy all the equations simultaneously. Can be linear or nonli…
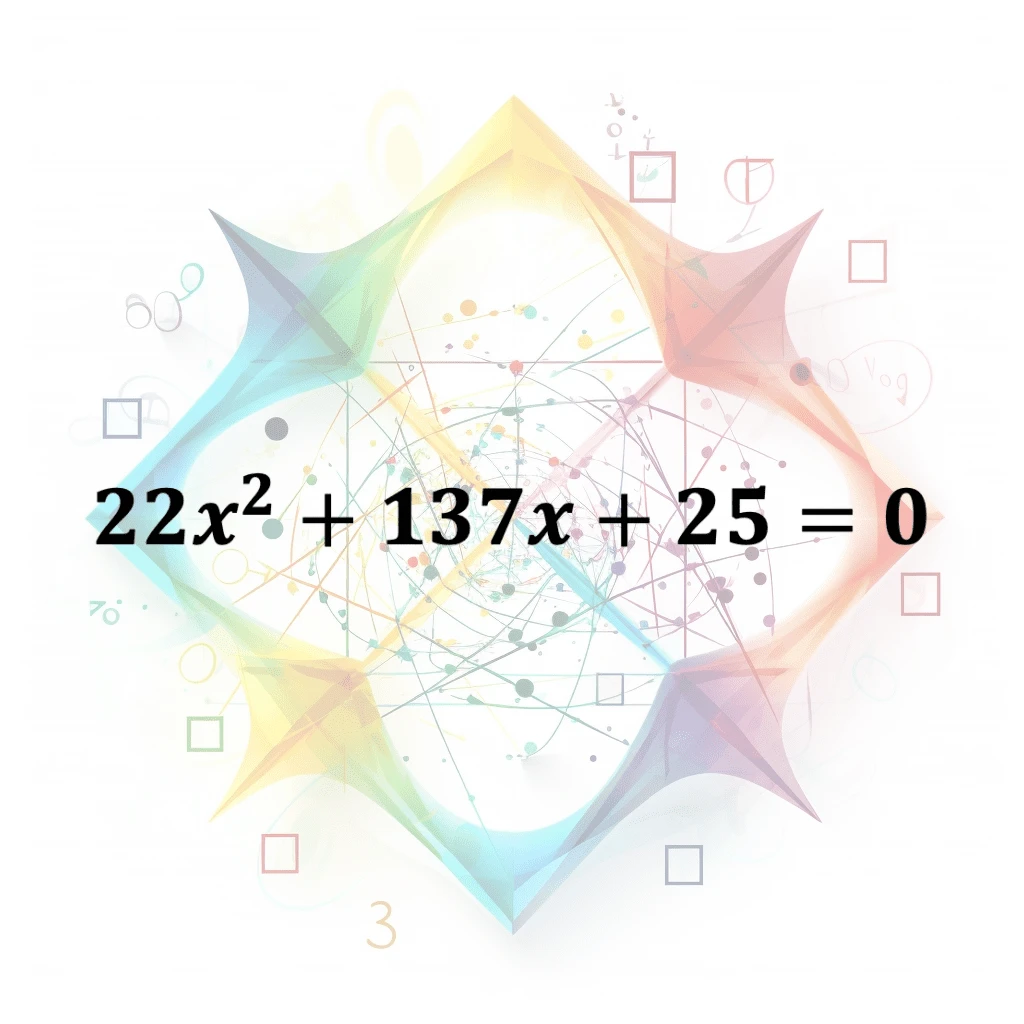
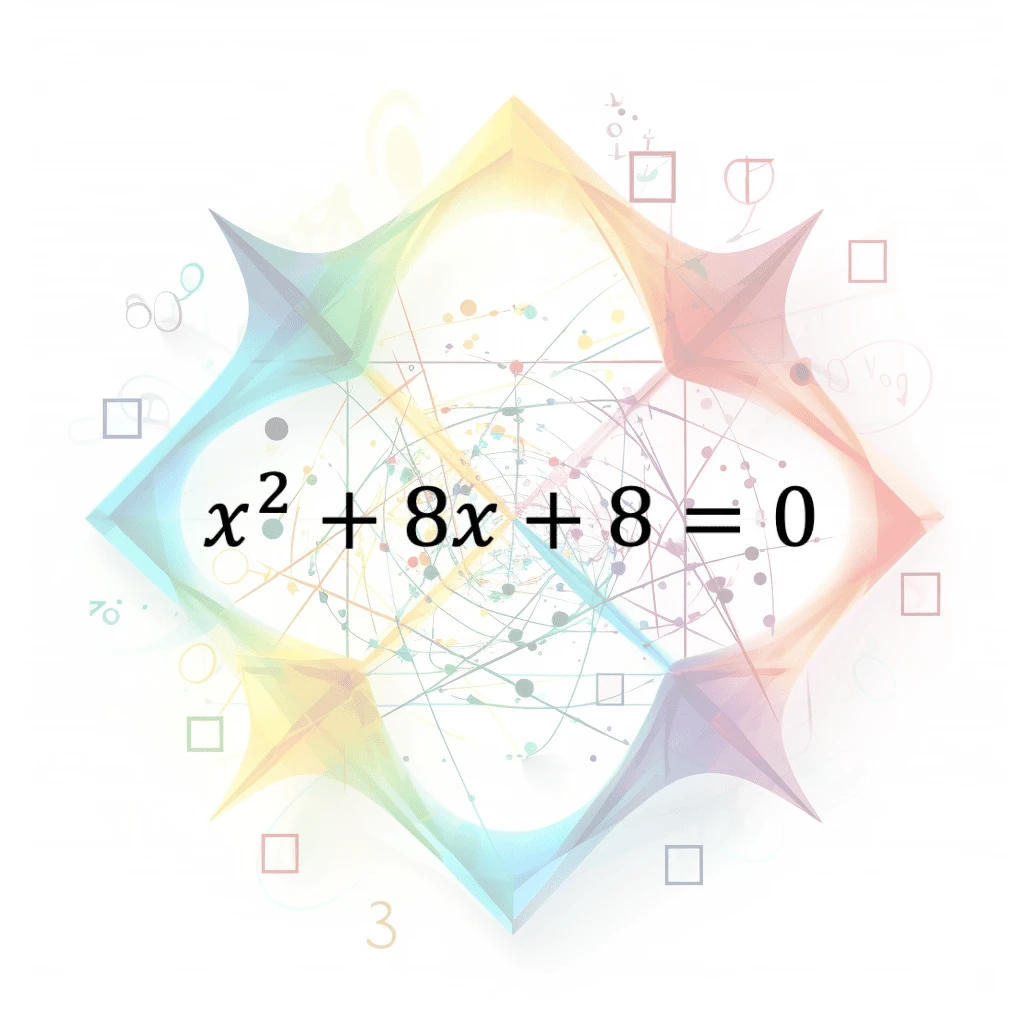
Quadratic Equation
A polynomial equation of the second degree in a single variable, typically in the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are coefficients and x is the unknown variable. Can be solved using various…
Intersection Of Two Lines
The point at which two lines in a Cartesian coordinate system meet or cross each other, representing the solution to a system of two linear equations in two variables.
Angle Regular Polygon
The interior angle of a regular polygon is the angle between two adjacent sides of the polygon.
Sector Area
The area of a sector of a circle is the measure of the amount of space inside the sector, which is a portion of the circle enclosed by two radii and an arc.
Area Of Circle Given Center A…
The area of a circle given the center and a point on the circle is the measure of the amount of space inside the circle, given the center and one point on the circle.
Curved Surface Area Cylinder
The curved surface area of a cylinder is the area of the lateral surface of the cylinder, which does not include the top and bottom faces.
Surface Area Cone
The surface area of a cone is the total area of all its faces, including the base and lateral surface.
Surface Area Pyramid
The surface area of a pyramid is the total area of all its faces, including the base and lateral surface.
Basic Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the sides and angles of triangles.
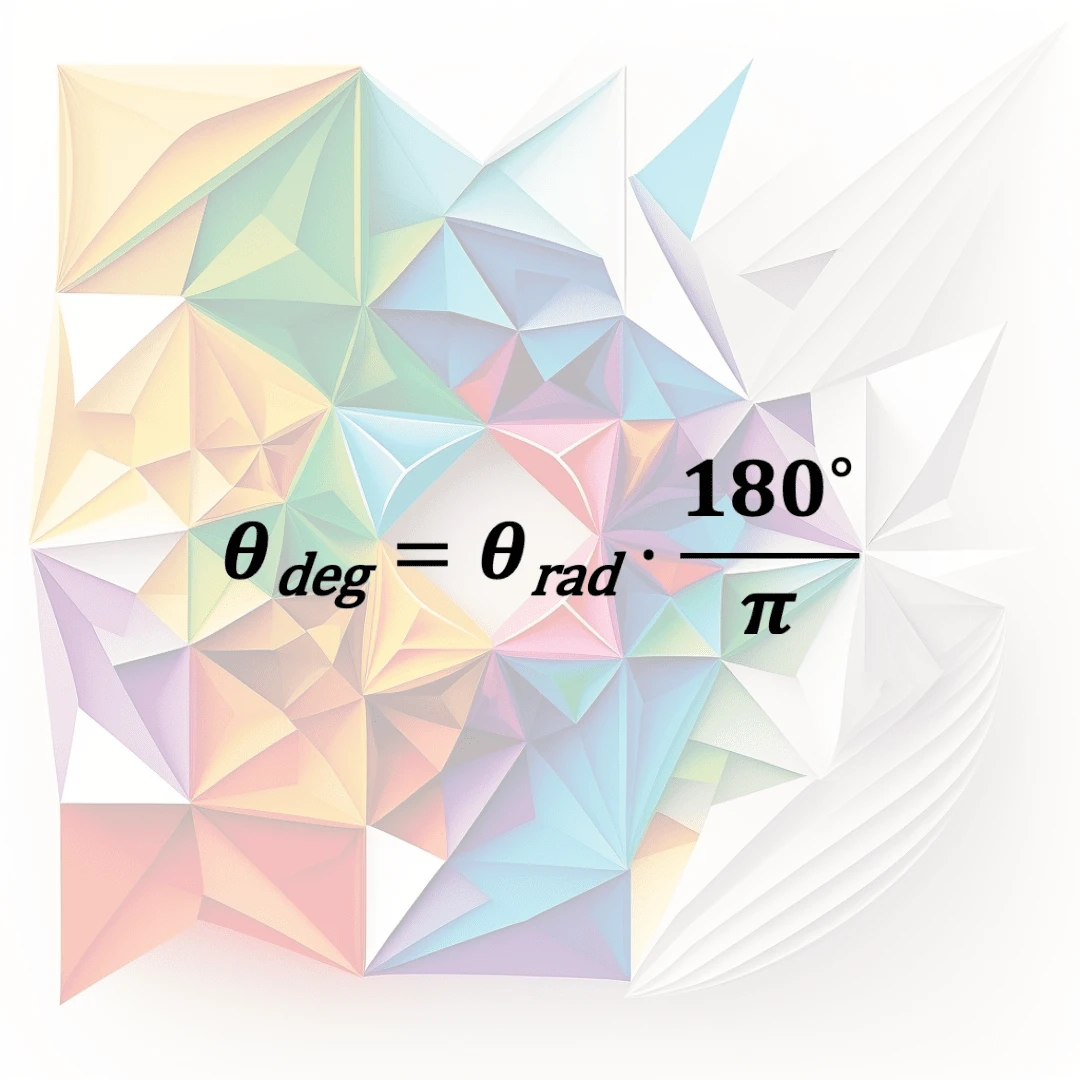
Degree To Rad
The conversion from degrees to radians is a way to express angles in terms of the ratio of the length of an arc of a circle to the radius of the circle.
Radian To Deg
The conversion from radians to degrees is a way to express angles in terms of degrees instead of radians.
Compound Interest
Compound interest is the amount of interest calculated on the initial principal amount, as well as on the accumulated interest from previous periods. It is calculated based on the compound interest f…
Dice Sum Probability
When two dice are rolled at the same time, there are a total of 6×6=36 possible outcomes. Out of these 36 outcomes, there are 4 ways to get a sum of 5: (1,4), (2,3), (3,2), and (4,1). Therefore, the …
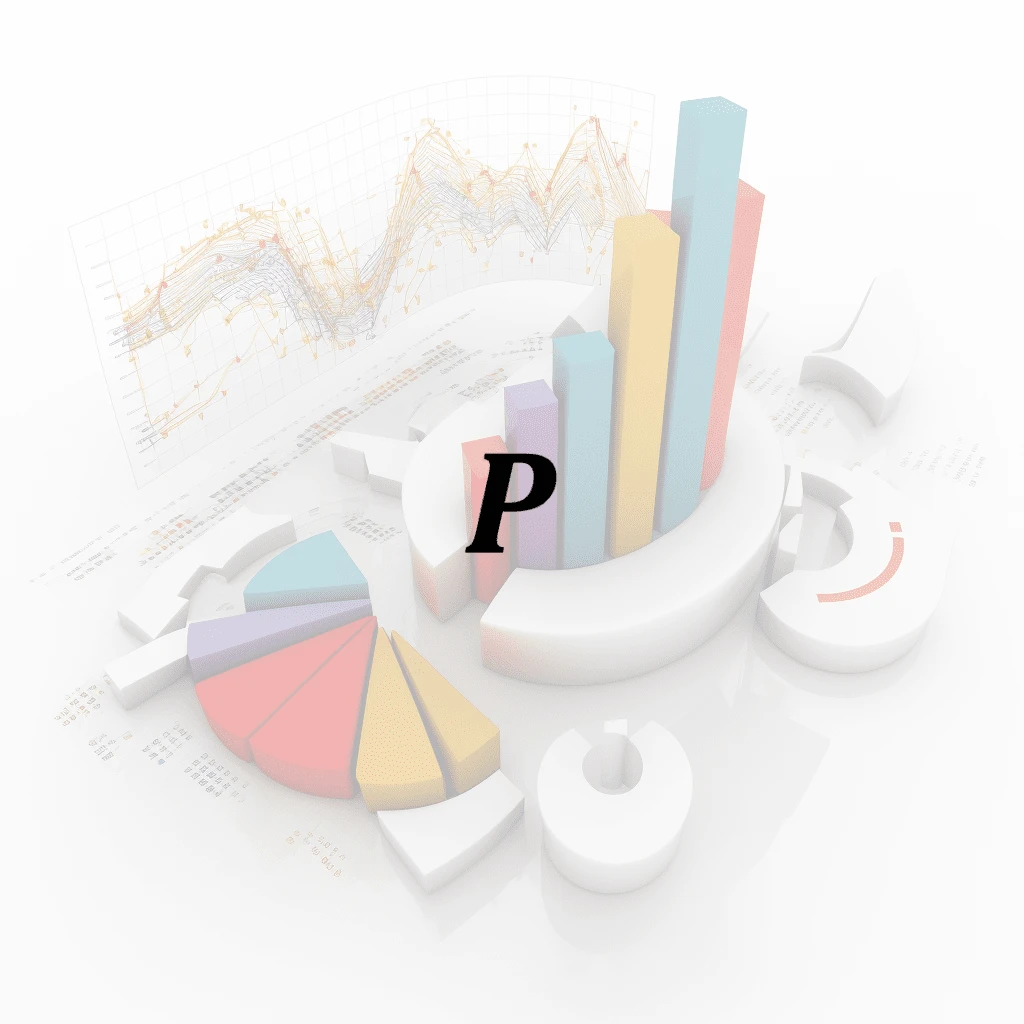
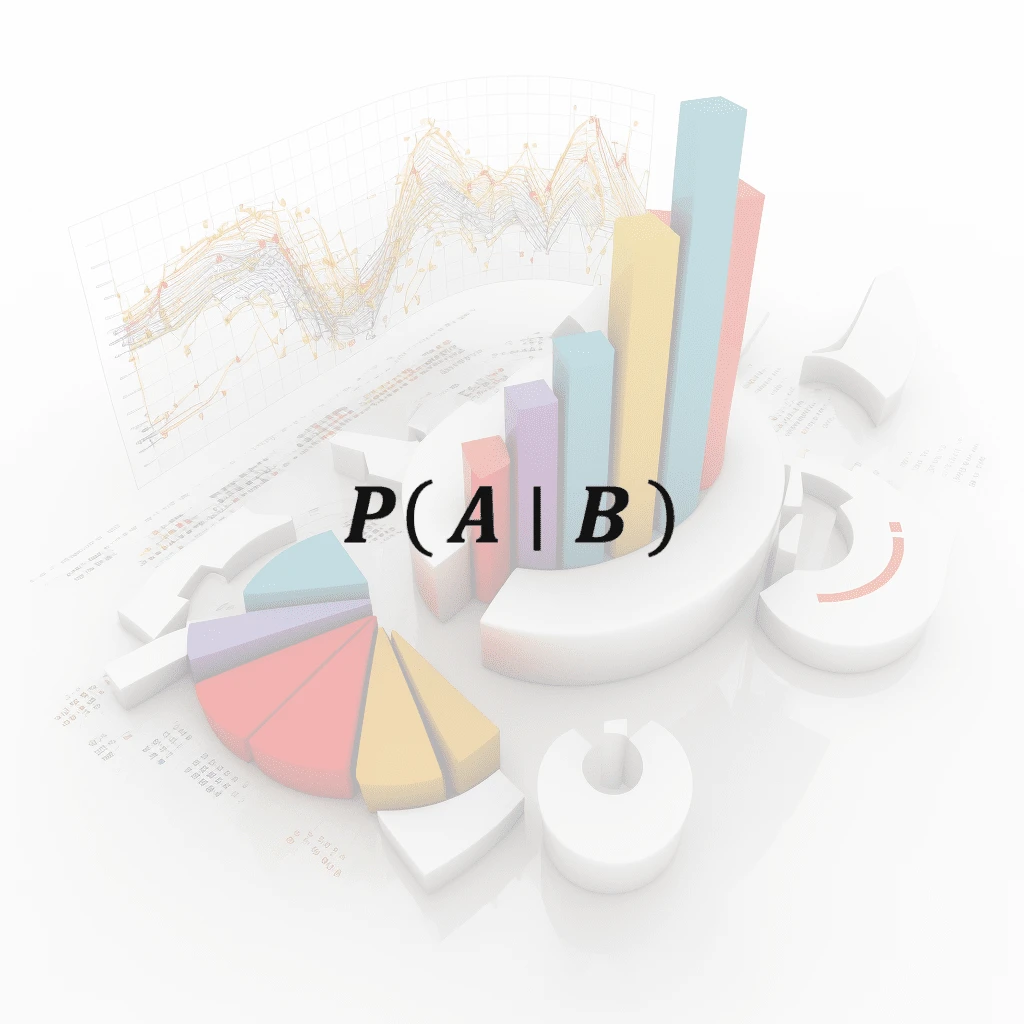
Conditional Probability
Conditional probability is the probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred. It is calculated by dividing the probability of both events occurring by the probabilit…
Confidence Interval
The confidence interval for sample [234, 223, 210, 203, 258, 299, 281, 208, 278, 252, 295, 245, 280, 235, 219, 297, 214, 267, 212, 256, 232, 221] with 99% confidence is (263.31, 229.33)
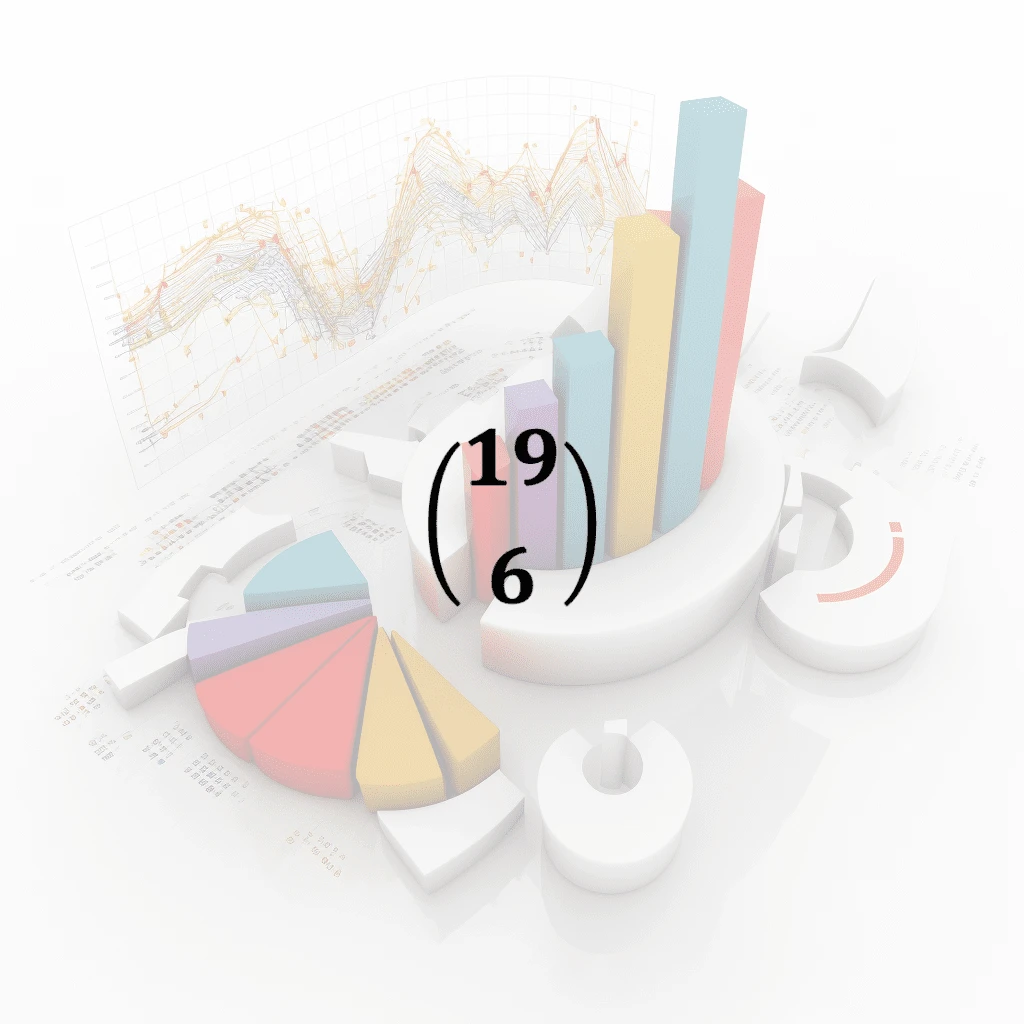
Combinations
In mathematics, a combination is a way of selecting items from a larger set where the order of the items does not matter. The number of combinations of n items taken k at a time is calculated using t…
Permutation
A permutation is an arrangement of objects in a specific order. The number of permutations of n objects taken r at a time is calculated using the formula nPr=n!/(n−r)!, where n! is the factorial of …
Fibonacci Series
The Fibonacci series is a sequence of numbers in which each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers, starting from 0 and 1. The series typically starts with 0, 1, and then each subsequent numb…
Binary To Hex
Binary to hexadecimal conversion is the process of converting a binary number to its equivalent hexadecimal (base 16) representation. This involves grouping the bits of the binary number in groups of…
bcd To Decimal
Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers in which each decimal digit is represented by a fixed number of binary digits. BCD to Decimal conversion is a process of c…
Decimal To bcd
Binary-Coded Decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each decimal digit is represented by a fixed number of binary bits. Decimal to BCD conversion is the process of conv…
Binary 2s Complement
The 2s complement of a binary number is a way to represent signed integers in binary form. It involves inverting all the bits (changing 0s to 1s and vice versa) of the original binary number and addi…
Binary Complement 1s
The 1s complement of a binary number is obtained by inverting all the bits (changing 0s to 1s and vice versa) of the original binary number. For example, the 1s complement of the binary number 1101 w…
Decimal To Hexadeci
Decimal to hexadecimal conversion is the process of converting a decimal number to its equivalent hexadecimal (base 16) representation. This involves dividing the decimal number by 16 repeatedly and …
Decimal To Octal
Decimal to octal conversion is the process of converting a decimal number to its equivalent octal (base 8) representation. This involves dividing the decimal number by 8 repeatedly and recording the …
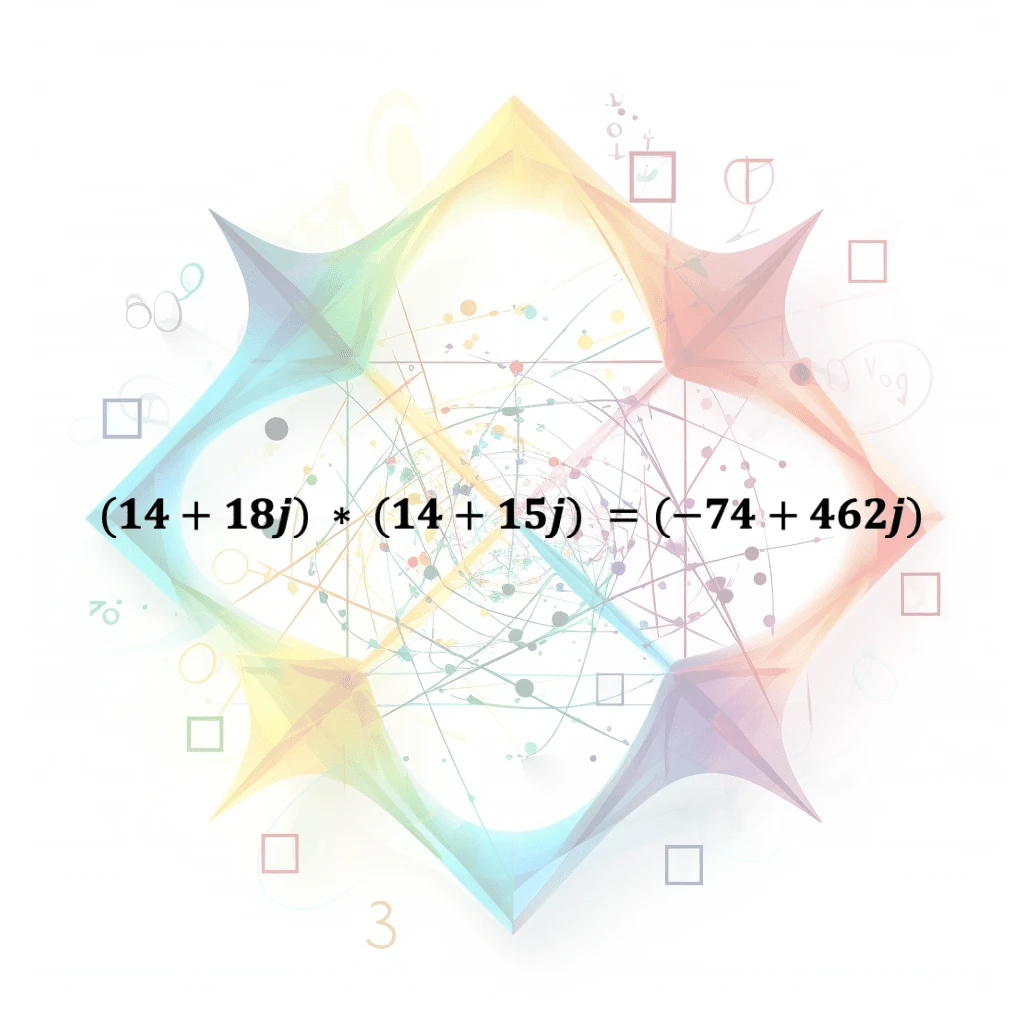
Multiply Complex Numbers
A mathematical operation that involves multiplying two complex numbers, which are numbers that consist of both a real part and an imaginary part. Involves applying the distributive property and the r…
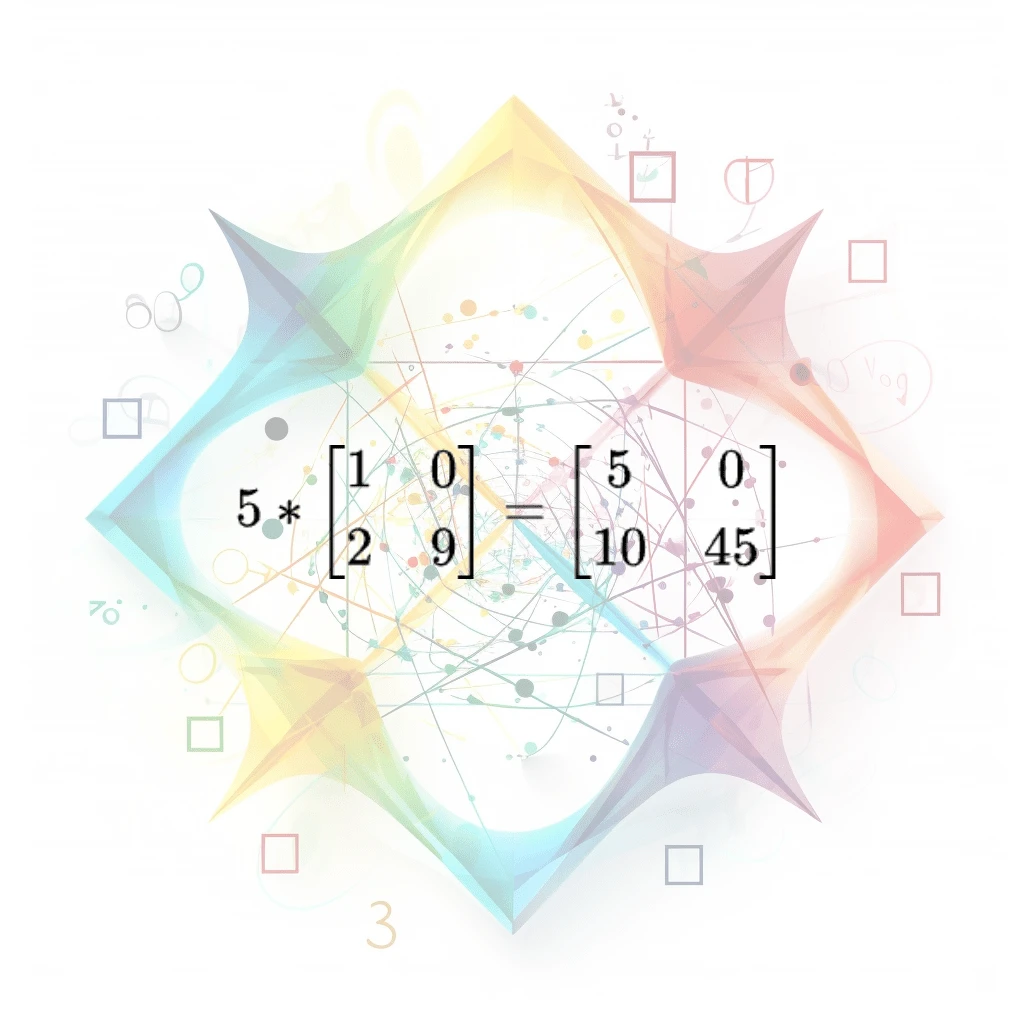
Multiply Integer to 2x2 Matrix
A mathematical operation that multiplies an integer scalar value with a 2x2 matrix, resulting in a new matrix where each element is multiplied by the scalar value. Used in linear algebra, graphics, a…
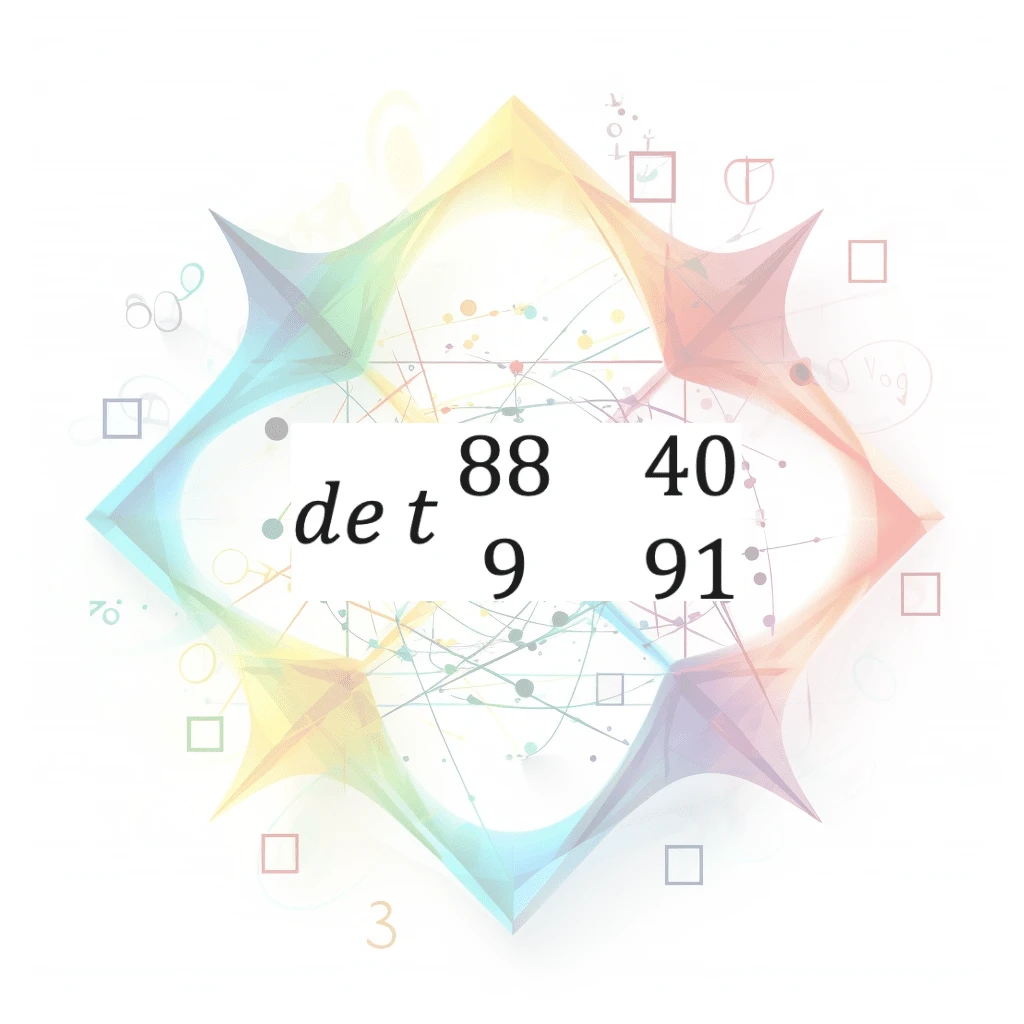
Determinant to 2x2 Matrix
A scalar value calculated from a 2x2 matrix, obtained by multiplying the elements of the main diagonal and subtracting the product of the off-diagonal elements. Provides information about the matrix'…
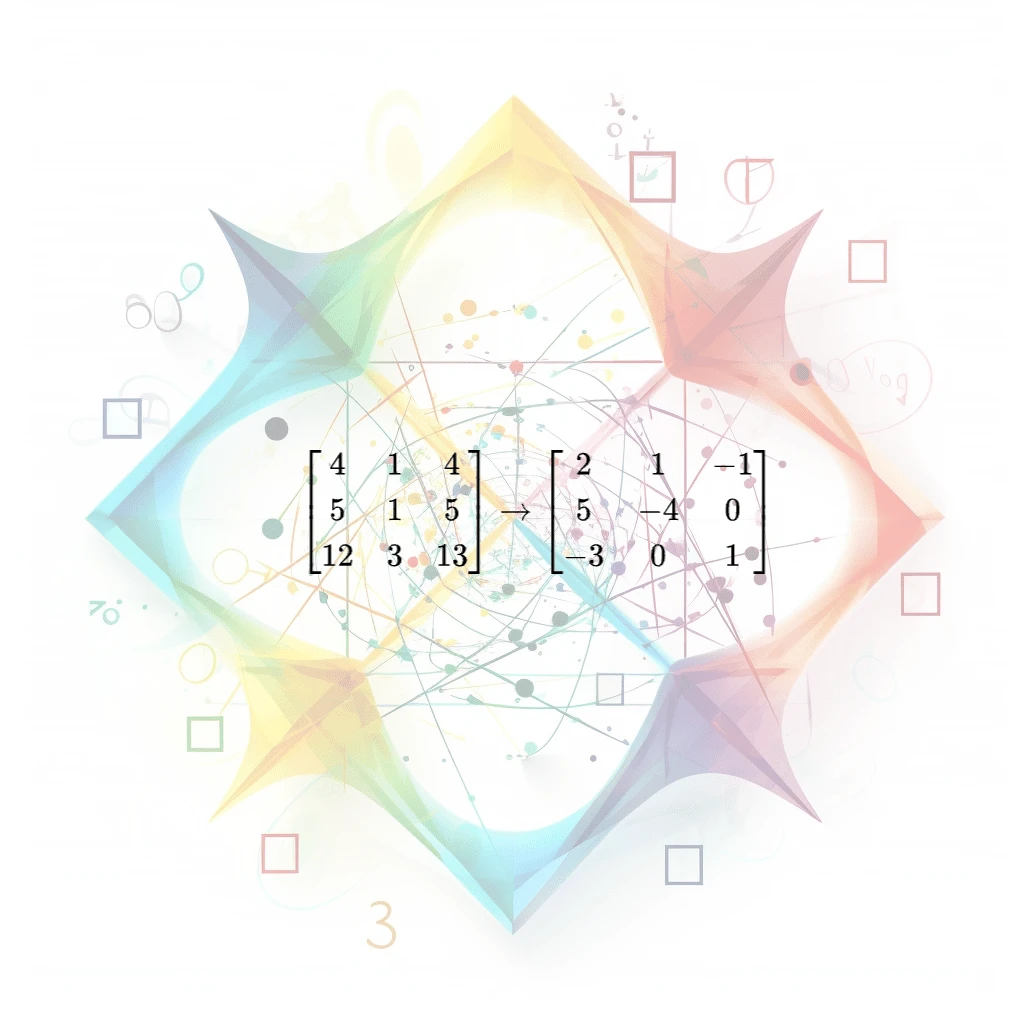
Invert Matrix
A mathematical operation that finds the inverse of a matrix, which is a matrix that, when multiplied with the original matrix, results in the identity matrix.
Power Rule Differentiation
In calculus, the power rule is a rule used for finding the derivative of a function that is a power of a variable. The power rule states that if a function f(x) is in the form of f(x) = x^n, where n …
Stationary Points
In calculus, stationary points, also known as critical points or turning points, are points on the graph of a function where the derivative is equal to zero or undefined. Stationary points are import…
Power Rule Integration
In calculus, the power rule for integration is a rule used for finding the antiderivative of a function that is a power of a variable. The power rule for integration states that if a function f(x) is…
Definite Integral
In calculus, the definite integral of a quadratic equation refers to the process of finding the accumulated area under the curve of a quadratic function within a specific interval, or the net signed …
Complex Quadratic
Complex quadratic refers to quadratic equations with complex (non-real) solutions. A quadratic equation is an equation of the form ax^2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants. When the discrim…
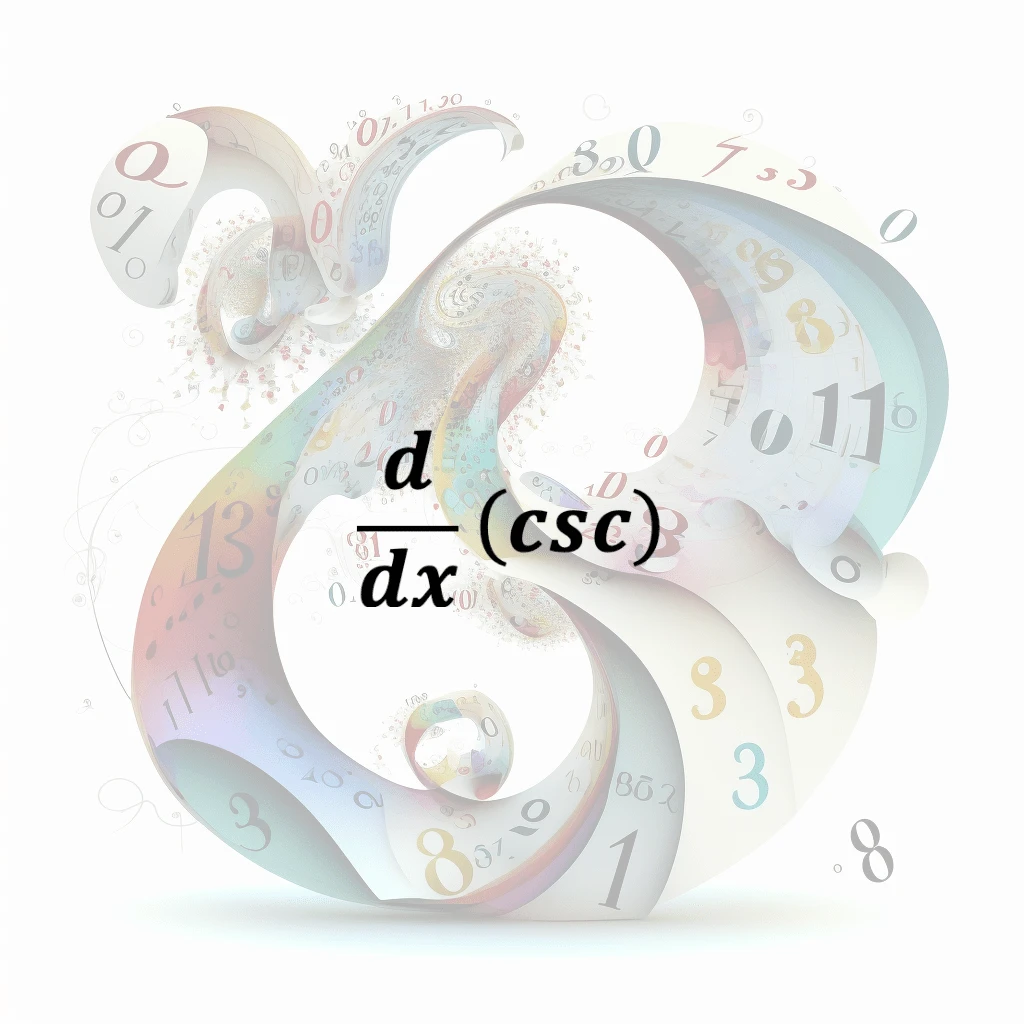
Trig Differentiation
In calculus, trigonometric differentiation refers to the process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, such as sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, or cosecant. Trigonometric fu…
Cross product of 2 vectors
A mathematical operation that calculates a vector that is perpendicular to the plane formed by two given vectors in three-dimensional space. The magnitude of the cross product is equal to the product…
Dot product of 2 vectors
A mathematical operation that calculates the scalar product of two vectors by multiplying their corresponding components and summing the results. Also known as the inner product or scalar product, th…
© 2023 AI MATH COACH